How To Prepare Income Statement

Preparing an Income Statement, also known as a statement of profit and Loss, involves summarizing your revenues (income) and expenses over a specific period to determine your net profit or net loss. This statement provides valuable insights into your business’s financial performance. Here’s how you can prepare a Statement of Profit and Loss, or income statement:
What is an Income statement?
A financial report describing a company’s income and expenses over a reporting period is called an income statement.
In other words, An income statement or statement of profit and loss shows the financial performance of an entity over a reporting period. As the name suggests, it provides a glimpse into which business activities brought in revenue and which cost the organization money.
It is usually prepared quarterly or annually and is also known as a profit and loss (P&L) statement.
The following details are commonly found on an income statement:
- Revenue: Revenue is the total amount of income generated by the business. Normally, this income is generated through the sale of goods or services related to the primary operations of the business. It is calculated by multiplying the average sales price by the number of items sold.
- Expenses: An expense is a business’s operational cost incurred to produce income.
- Costs of goods sold (COGS): This is the direct cost of producing the goods sold by a business. This amount also accounts for the cost of the materials and labor used directly to produce the items. It excludes indirect costs related to sales personnel and distribution, for example.
- Gross profit: Gross profit is the amount of money made after all expenses associated with creating and offering your products or services have been deducted. The formula to calculate gross profit is the total revenue minus the cost of goods sold (Gross Profit = Total Revenue – Total COGS)
- Operating income: Gross profit minus operating expenses
- Income before taxes: Operating income minus non-operating expenses
- Net income: This is income before taxes
- Earnings per share (EPS): It can be defined as the value of earnings per outstanding share of the company’s common stock. By displaying how much revenue a firm generates for each share of its stock, EPS reveals the company’s profitability. The formula for calculating it is to divide net income by the total number of outstanding shares.
- Depreciation: This is the value lost by assets, such as machinery, equipment, and property, over time
- EBITDA: Earnings before interest, depreciation, taxes, and amortization
Also Read: How To Prepare A Balance Sheet
Preparation of the Income Statement
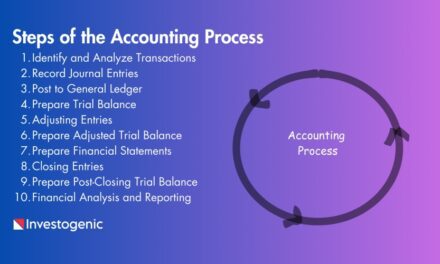
Step 1: Determine the Reporting Date and Period
First, you must decide the reporting period for which you want to prepare the income statement. Generally, the reporting period of the business is one fiscal year, but the income statement is also prepared monthly or quarterly.
Step 2: Understand the format of the Income statement.
Before you begin preparing an income statement or profit and loss statement, you must understand the format of the income statement. Through this, you will understand what data you need to collect and how to use this data.
It is possible to show the income statement in a “one-step” or “two-step” manner.
- One-step format: In this format, revenues and gains are grouped together, and expenses and losses are grouped together. These amounts are then totaled to show net income or loss.
- Two-step format: To illustrate line items that are important for making decisions, such as gross margin and operational income, apart from non-operating income and net income or loss, utilize subtotals. A “two-step” approach is used by many commercial and industrial reporting firms.

Step 3: Calculate Total Revenue
Next, you need to calculate the revenue generated by your business or organization during the reporting period.
If you prepare an income statement for a separate division of your business, you will calculate the revenue generated by that division, or the total revenue generated by the entire organization if you want to prepare an income statement for the entire organization.
Business revenue includes sales made by the business and other income earned by the business during the reporting period.
Step 4: Calculate the Cost of Goods Sold (COGS)
Then you required to calculate COGS of your business. All costs and expenses directly connected to the creation of commodities are included in the cost of goods sold (COGS). Indirect expenses like sales, marketing, and overhead are not included in COGS.
Step 5: Calculate Gross Profit
Next, you can calculate Gross profit. Gross profit is the amount of money made after all expenses associated with creating and offering your products or services have been deducted. The formula to calculate gross profit is the total revenue minus the cost of goods sold (Gross Profit = Total Revenue minus Total COGS).
Step 6: Calculate Operating Expenses
After calculating Gross profit, you required to calculate operating expenses. An expense incurred by a business as part of ongoing operations is known as an operating expense. Rent, furnishings, inventory costs, marketing, payroll, insurance, step charges, and money set aside for R&D are all examples of operating expenses.
Step 7: Ensure Accuracy
Double-check all calculations and data entries to ensure accuracy. Even a small error can significantly affect the final figures.
Step 8: Calculate Income
To calculate income, you need to subtract operating expenses from gross profit. This is the pretax income your business generated during the reporting period. This is also called earnings before interest and tax (EBIT).
Step 9: Calculate Interest and taxes.
Next, you are required to determine the interest charges and taxes on your business.
Interest refers to any charges your business must pay on the debt it owes. Taxes include local, state, and federal taxes, as well as any payroll taxes for your business.
Step 10: Calculate Net income.
The final step or purpose of preparing the income statement is to calculate the net income for the reporting period. To do this, subtract interest and then taxes from your EBIT to get your business’s net income, or available funds, as the remaining number.
It can be used for various purposes for business needs, such as distribution as a dividend to shareholders, adding to reserves, etc.
Analyze the Results
Once you have prepared the Statement of Profit and Loss, analyze the figures to gain insights into your business’s financial performance. Compare the current period’s results with previous periods and industry benchmarks to assess how well your business is doing.